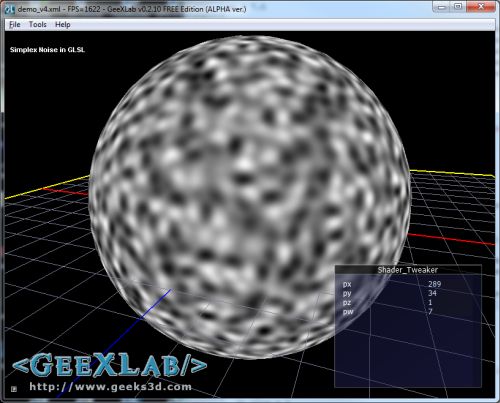
Simplex noise is an improved version of Perlin noise. Compared to Perlin noise, simplex noise has the following advantages:
- simplex noise has a lower computational complexity and requires fewer multiplications.
- Simplex noise scales to higher dimensions (4D, 5D and up) with much less computational cost, the complexity is for dimensions instead of the of classic noise.
- Simplex noise has no noticeable directional artifacts.
- Simplex noise has a well-defined and continuous gradient everywhere that can be computed quite cheaply.
- Simplex noise is easy to implement in hardware
For a detailed explanation about simplex noise, here is a nice PDF: Simplex noise demystified. Here is a thread on OpenGL forum about this topic.
As usual, I quickly coded a small GeeXLab demo to test the simplex noise GLSL shader. The demo is available in GeeXLab code samples pack (GLSL_Simplex_Noise/ folder). You can download the complete code sample pack from this page or here:
[download#40#image]
Just start GeeXLab and load (or drag and drop) the DEMO.xml file in GeeXLab. That’s all!
You can find other shaders here: Shader Library.
Here is the complete GLSL shader (vertex and fragment shaders):
[Vertex_Shader]
varying vec2 v_texCoord2D;
varying vec3 v_texCoord3D;
varying vec4 v_color;
void main()
{
gl_Position = gl_ModelViewProjectionMatrix *
gl_Vertex.xyz;
v_texCoord2D = gl_MultiTexCoord0.xy;
v_texCoord3D = gl_Vertex.xyz * 0.05;
v_color = gl_Color;
}
[Pixel_Shader]
#define NORMALIZE_GRADIENTS
#undef USE_CIRCLE
#define COLLAPSE_SORTNET
float permute(float x0,vec3 p) {
float x1 = mod(x0 * p.y, p.x);
return floor( mod( (x1 + p.z) *x0, p.x ));
}
vec2 permute(vec2 x0,vec3 p) {
vec2 x1 = mod(x0 * p.y, p.x);
return floor( mod( (x1 + p.z) *x0, p.x ));
}
vec3 permute(vec3 x0,vec3 p) {
vec3 x1 = mod(x0 * p.y, p.x);
return floor( mod( (x1 + p.z) *x0, p.x ));
}
vec4 permute(vec4 x0,vec3 p) {
vec4 x1 = mod(x0 * p.y, p.x);
return floor( mod( (x1 + p.z) *x0, p.x ));
}
uniform vec4 pParam;
// Example constant with a 289 element permutation
//const vec4 pParam = vec4( 17.0*17.0, 34.0, 1.0, 7.0);
float taylorInvSqrt(float r)
{
return ( 0.83666002653408 + 0.7*0.85373472095314 - 0.85373472095314 * r );
}
float simplexNoise2(vec2 v)
{
const vec2 C = vec2(0.211324865405187134, // (3.0-sqrt(3.0))/6.;
0.366025403784438597); // 0.5*(sqrt(3.0)-1.);
const vec3 D = vec3( 0., 0.5, 2.0) * 3.14159265358979312;
// First corner
vec2 i = floor(v + dot(v, C.yy) );
vec2 x0 = v - i + dot(i, C.xx);
// Other corners
vec2 i1 = (x0.x > x0.y) ? vec2(1.,0.) : vec2(0.,1.) ;
// x0 = x0 - 0. + 0. * C
vec2 x1 = x0 - i1 + 1. * C.xx ;
vec2 x2 = x0 - 1. + 2. * C.xx ;
// Permutations
i = mod(i, pParam.x);
vec3 p = permute( permute(
i.y + vec3(0., i1.y, 1. ), pParam.xyz)
+ i.x + vec3(0., i1.x, 1. ), pParam.xyz);
#ifndef USE_CIRCLE
// ( N points uniformly over a line, mapped onto a diamond.)
vec3 x = fract(p / pParam.w) ;
vec3 h = 0.5 - abs(x) ;
vec3 sx = vec3(lessThan(x,D.xxx)) *2. -1.;
vec3 sh = vec3(lessThan(h,D.xxx));
vec3 a0 = x + sx*sh;
vec2 p0 = vec2(a0.x,h.x);
vec2 p1 = vec2(a0.y,h.y);
vec2 p2 = vec2(a0.z,h.z);
#ifdef NORMALISE_GRADIENTS
p0 *= taylorInvSqrt(dot(p0,p0));
p1 *= taylorInvSqrt(dot(p1,p1));
p2 *= taylorInvSqrt(dot(p2,p2));
#endif
vec3 g = 2.0 * vec3( dot(p0, x0), dot(p1, x1), dot(p2, x2) );
#else
// N points around a unit circle.
vec3 phi = D.z * mod(p,pParam.w) /pParam.w ;
vec4 a0 = sin(phi.xxyy+D.xyxy);
vec2 a1 = sin(phi.zz +D.xy);
vec3 g = vec3( dot(a0.xy, x0), dot(a0.zw, x1), dot(a1.xy, x2) );
#endif
// mix
vec3 m = max(0.5 - vec3(dot(x0,x0), dot(x1,x1), dot(x2,x2)), 0.);
m = m*m ;
return 1.66666* 70.*dot(m*m, g);
}
float simplexNoise3(vec3 v)
{
const vec2 C = vec2(1./6. , 1./3. ) ;
const vec4 D = vec4(0., 0.5, 1.0, 2.0);
// First corner
vec3 i = floor(v + dot(v, C.yyy) );
vec3 x0 = v - i + dot(i, C.xxx) ;
// Other corners
#ifdef COLLAPSE_SORTNET
vec3 g = vec3( greaterThan( x0.xyz, x0.yzx) );
vec3 l = vec3( lessThanEqual( x0.xyz, x0.yzx) );
vec3 i1 = g.xyz * l.zxy;
vec3 i2 = max( g.xyz, l.zxy);
#else
// Keeping this clean - let the compiler optimize.
vec3 q1;
q1.x = max(x0.x, x0.y);
q1.y = min(x0.x, x0.y);
q1.z = x0.z;
vec3 q2;
q2.x = max(q1.x,q1.z);
q2.z = min(q1.x,q1.z);
q2.y = q1.y;
vec3 q3;
q3.y = max(q2.y, q2.z);
q3.z = min(q2.y, q2.z);
q3.x = q2.x;
vec3 i1 = vec3(equal(q3.xxx, x0));
vec3 i2 = i1 + vec3(equal(q3.yyy, x0));
#endif
// x0 = x0 - 0. + 0. * C
vec3 x1 = x0 - i1 + 1. * C.xxx;
vec3 x2 = x0 - i2 + 2. * C.xxx;
vec3 x3 = x0 - 1. + 3. * C.xxx;
// Permutations
i = mod(i, pParam.x );
vec4 p = permute( permute( permute(
i.z + vec4(0., i1.z, i2.z, 1. ), pParam.xyz)
+ i.y + vec4(0., i1.y, i2.y, 1. ), pParam.xyz)
+ i.x + vec4(0., i1.x, i2.x, 1. ), pParam.xyz);
// Gradients
// ( N*N points uniformly over a square, mapped onto a octohedron.)
float n_ = 1.0/pParam.w ;
vec3 ns = n_ * D.wyz - D.xzx ;
vec4 j = p - pParam.w*pParam.w*floor(p * ns.z *ns.z); // mod(p,N*N)
vec4 x_ = floor(j * ns.z) ;
vec4 y_ = floor(j - pParam.w * x_ ) ; // mod(j,N)
vec4 x = x_ *ns.x + ns.yyyy;
vec4 y = y_ *ns.x + ns.yyyy;
vec4 h = 1. - abs(x) - abs(y);
vec4 b0 = vec4( x.xy, y.xy );
vec4 b1 = vec4( x.zw, y.zw );
vec4 s0 = vec4(lessThan(b0,D.xxxx)) *2. -1.;
vec4 s1 = vec4(lessThan(b1,D.xxxx)) *2. -1.;
vec4 sh = vec4(lessThan(h, D.xxxx));
vec4 a0 = b0.xzyw + s0.xzyw*sh.xxyy ;
vec4 a1 = b1.xzyw + s1.xzyw*sh.zzww ;
vec3 p0 = vec3(a0.xy,h.x);
vec3 p1 = vec3(a0.zw,h.y);
vec3 p2 = vec3(a1.xy,h.z);
vec3 p3 = vec3(a1.zw,h.w);
#ifdef NORMALISE_GRADIENTS
p0 *= taylorInvSqrt(dot(p0,p0));
p1 *= taylorInvSqrt(dot(p1,p1));
p2 *= taylorInvSqrt(dot(p2,p2));
p3 *= taylorInvSqrt(dot(p3,p3));
#endif
// Mix
vec4 m = max(0.6 - vec4(dot(x0,x0), dot(x1,x1), dot(x2,x2), dot(x3,x3)), 0.);
m = m * m;
//used to be 64.
return 48.0 * dot( m*m, vec4( dot(p0,x0), dot(p1,x1),
dot(p2,x2), dot(p3,x3) ) );
}
vec4 grad4(float j, vec4 ip)
{
const vec4 ones = vec4(1.,1.,1.,-1.);
vec4 p,s;
p.xyz = floor( fract (vec3(j) * ip.xyz) *pParam.w) * ip.z -1.0;
p.w = 1.5 - dot(abs(p.xyz), ones.xyz);
s = vec4(lessThan(p,vec4(0.)));
p.xyz = p.xyz + (s.xyz*2.-1.) * s.www;
return p;
}
float simplexNoise4(vec4 v)
{
const vec2 C = vec2( 0.138196601125010504,
0.309016994374947451);
// First corner
vec4 i = floor(v + dot(v, C.yyyy) );
vec4 x0 = v - i + dot(i, C.xxxx);
// Other corners
// Force existance of strict total ordering in sort.
vec4 q0 = floor(x0 * 1024.0) + vec4( 0., 1./4., 2./4. , 3./4.);
vec4 q1;
q1.xy = max(q0.xy,q0.zw); // x:z y:w
q1.zw = min(q0.xy,q0.zw);
vec4 q2;
q2.xz = max(q1.xz,q1.yw); // x:y z:w
q2.yw = min(q1.xz,q1.yw);
vec4 q3;
q3.y = max(q2.y,q2.z); // y:z
q3.z = min(q2.y,q2.z);
q3.xw = q2.xw;
vec4 i1 = vec4(lessThanEqual(q3.xxxx, q0));
vec4 i2 = vec4(lessThanEqual(q3.yyyy, q0));
vec4 i3 = vec4(lessThanEqual(q3.zzzz, q0));
// x0 = x0 - 0. + 0. * C
vec4 x1 = x0 - i1 + 1. * C.xxxx;
vec4 x2 = x0 - i2 + 2. * C.xxxx;
vec4 x3 = x0 - i3 + 3. * C.xxxx;
vec4 x4 = x0 - 1. + 4. * C.xxxx;
// Permutations
i = mod(i, pParam.x );
float j0 = permute( permute( permute( permute (
i.w, pParam.xyz) + i.z, pParam.xyz)
+ i.y, pParam.xyz) + i.x, pParam.xyz);
vec4 j1 = permute( permute( permute( permute (
i.w + vec4(i1.w, i2.w, i3.w, 1. ), pParam.xyz)
+ i.z + vec4(i1.z, i2.z, i3.z, 1. ), pParam.xyz)
+ i.y + vec4(i1.y, i2.y, i3.y, 1. ), pParam.xyz)
+ i.x + vec4(i1.x, i2.x, i3.x, 1. ), pParam.xyz);
// Gradients
// ( N*N*N points uniformly over a cube,
// mapped onto a 4-octohedron.)
vec4 ip = pParam ;
ip.xy *= pParam.w ;
ip.x *= pParam.w ;
ip = vec4(1.,1.,1.,2.) / ip ;
vec4 p0 = grad4(j0, ip);
vec4 p1 = grad4(j1.x, ip);
vec4 p2 = grad4(j1.y, ip);
vec4 p3 = grad4(j1.z, ip);
vec4 p4 = grad4(j1.w, ip);
#ifdef NORMALISE_GRADIENTS
p0 *= taylorInvSqrt(dot(p0,p0));
p1 *= taylorInvSqrt(dot(p1,p1));
p2 *= taylorInvSqrt(dot(p2,p2));
p3 *= taylorInvSqrt(dot(p3,p3));
p4 *= taylorInvSqrt(dot(p4,p4));
#endif
// Mix
vec3 m0 = max(0.6 - vec3(dot(x0,x0), dot(x1,x1), dot(x2,x2)), 0.);
vec2 m1 = max(0.6 - vec2(dot(x3,x3), dot(x4,x4) ), 0.);
m0 = m0 * m0;
m1 = m1 * m1;
return 32. * (dot(m0*m0, vec3(dot(p0, x0), dot(p1, x1), dot(p2, x2)))
+ dot(m1*m1, vec2(dot(p3, x3), dot(p4, x4)))) ;
}
uniform float time;
varying vec2 v_texCoord2D;
varying vec3 v_texCoord3D;
varying vec4 v_color;
void main(void)
{
vec3 v = vec3(2.0 * v_texCoord3D.xyz * (2.0 + sin(0.5*time)));
float n = simplexNoise3(v);
gl_FragColor = v_color * vec4(0.5 + 0.5 * vec3(n, n, n), 1.0);
}
This is cool stuff. Finally noise() in GLSL that is fast and decent!
Cool! Thanks!
This code has been taken from https://github.com/ashima/webgl-noise in violation of the MIT Expat license. Please see https://github.com/ashima/webgl-noise for the latest Perlin and simplex noise shaders with performance improvements and bug fixes.