Futuremark has updated 3DMark with a new test focused on NVIDIA Deep Learning Super Sampling or DLSS. NVIDIA DLSS is a anti-aliasing technique that uses the power of deep learning and AI to improve game performance while maintaining visual quality. NVIDIA DLSS requires a NVIDIA GeForce RTX.
Deep Learning Super Sampling (DLSS) is an NVIDIA RTX technology that uses deep learning and AI to improve game performance while maintaining visual quality. DLSS uses a deep neural network to extract multidimensional features of the rendered scene and intelligently combine details from multiple frames to construct a high-quality final image. This approach allows NVIDIA RTX GPUs to use fewer samples for rendering and use AI to fill in information to create the final image. The result is a clear, crisp image of a quality similar to traditional rendering but with higher performance.
Aliasing
Aliasing — a distracting jagged line on the edge of an object in a scene — is a common artifact in real-time computer graphics. Increasing the resolution of the entire image is not always practical so a common way to remove the jagged lines is to increase the number of samples on the line which helps to smooth it. Many techniques have been developed which intelligently blend the colors of the jagged edges with the colors of nearby pixels but most of these can lead to a loss of fine detail.Temporal Anti-aliasing
The 3DMark Port Royal benchmark uses Temporal Anti-Aliasing (TAA), a popular anti-aliasing technique used in many games today. TAA solves the aliasing problem by accumulating multiple samples temporally — instead of adding more samples to a single frame, it adds a small jitter to a rendered frame, and combines the current samples with matching samples from previous frames. This directly leads to an increased sampling rate. Unfortunately, TAA suffers from flickering and ghosting artifacts. These can be especially seen in dynamic scenes.A deep learning solution to aliasing
To develop Deep Learning Super Sampling, NVIDIA researchers trained a neural network to find jagged edges in an image, determine the best color for each pixel, and then apply proper colors to create smoother edges and improved image quality. DLSS provides high-quality anti-aliasing with fewer artifacts and better performance than other types of anti-aliasing. Compared with TAA, DLSS produces sharp images that are temporally stable.Neural network training
The specific details and method of the training is NVIDIA’s trade secret since DLSS is a proprietary technology. In general terms, the training process utilizes a large set of supersampled aliased rendering results and screen-space velocity textures generated by the workload to train the weights of the convolutional autoencoder.
The new DLSS test is available in 3DMark 2.8.6427.0 (Professional version).
The complete test includes two parts: the first run renders Port Royal to the output resolution with DLSS disabled to measure baseline performance. The second run renders Port Royal at a lower resolution then uses DLSS processing to create frames at the output resolution.

I ran the test on a GeForce RTX 2070 with latest GeForce 418.81 graphics drivers. I let the default resolution (2560 x 1440).
Here is the result:

Look at the score when DLSS is ON: more or less 50% faster… I think this is essentially due to the low DLSS rendering resolution (1920×1080) even if the final rendering (output resolution) is scaled to 2560×1440.
I used 3DMark Image Quality Tool to record some frames (DLSS OFF/ON). Here a detail of the frame 36 (recorded at 3840×2160 because I have a 4k monitor on my test system and because of the issues with the Image Quality Tool and NVIDIA drivers).
DLSS OFF
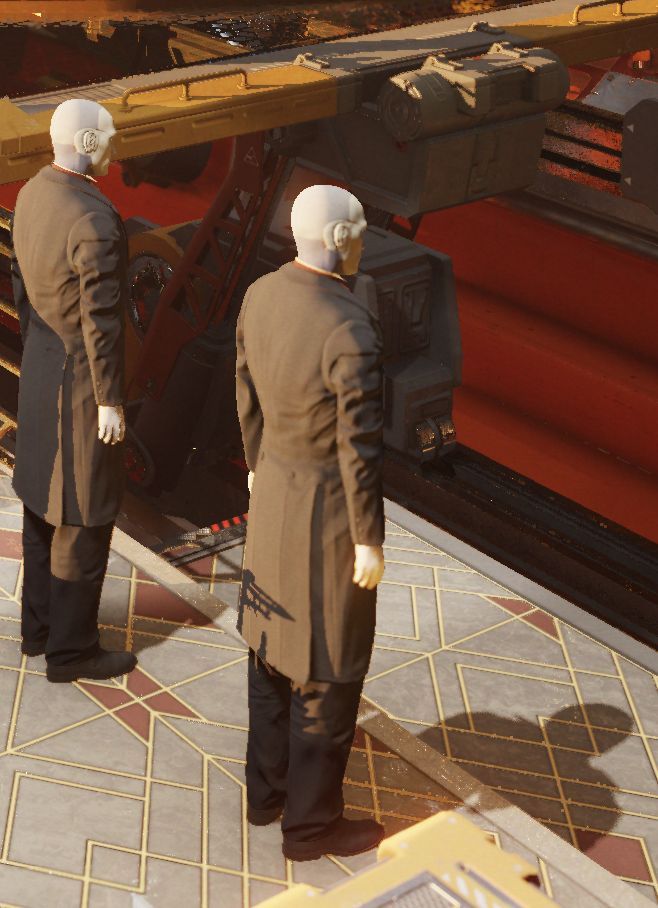

DLSS ON
